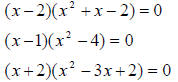Equilibrium analysis
Chapter 3 – Equilibrium analysis (algebra review)
What is equilibrium? In a specified model, a lack of tendency to change.
This is static equilibrium – study of statics.
Is equilibrium desirable? Depends.
Partial equilibrium – only part of model considered, ie ceteris paribus.
Solving a linear model
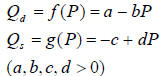
Graph:
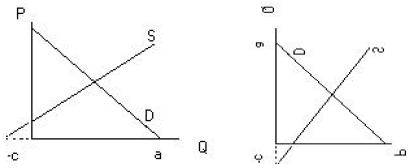 |
|
| Economics | “Right” way |
No excess demand or supply implies that
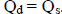 , so
, so
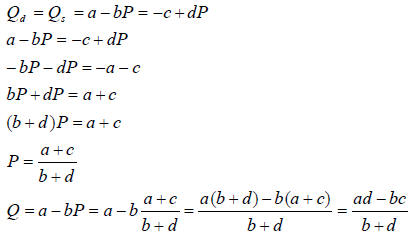
This is the intersection of sets
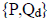 and
and 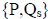
A non-linear example
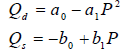
The demand function is a quadratic function
Only non-negative P’s and Q’s are considered so the demand curve is a segment of
a parabola.
Graph:
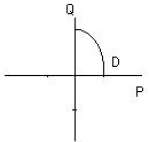
Excess demand = 0, so
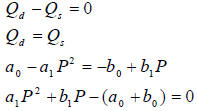
The above is a quadratic equation that can be written as
aP2 + bP + c = 0
To solve for P:
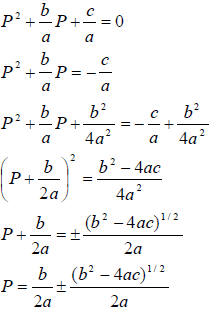
The quadratic formula! A good formula to memorize.
Try this one:
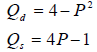
Answer: P = 1, Q = 3
Higher degree polynomials
Factoring by trial and error
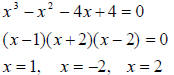
Find a factor, then use quadratic formula or find another factor: